Define Fluorescence Microscopy

A fluorescent surface substance or colour has a very bright appearance when light is.
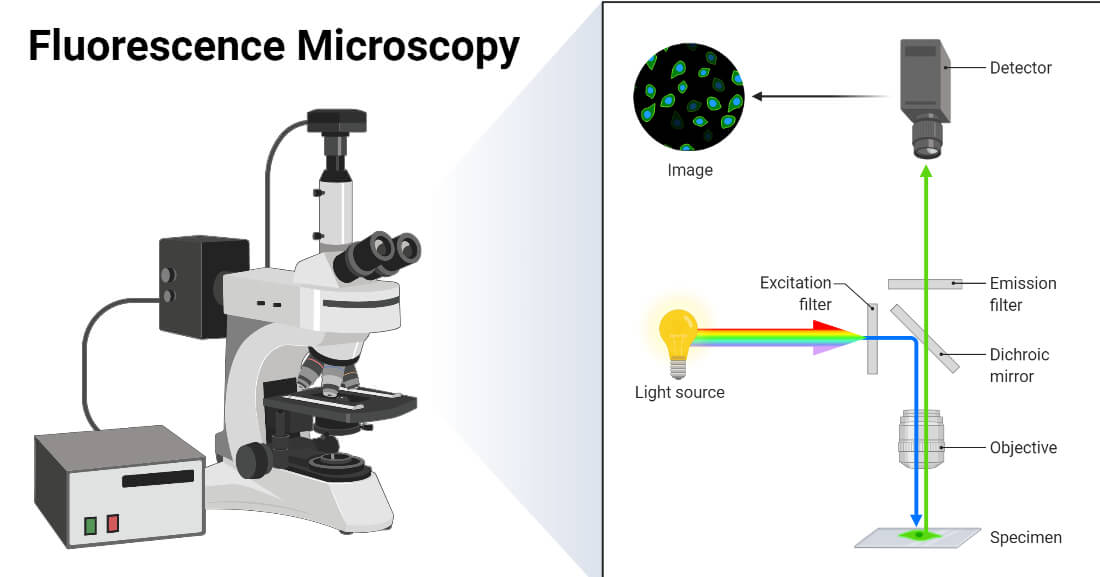
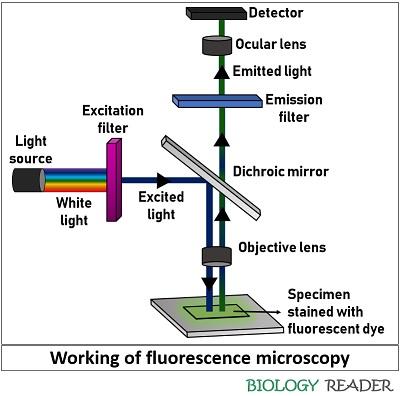
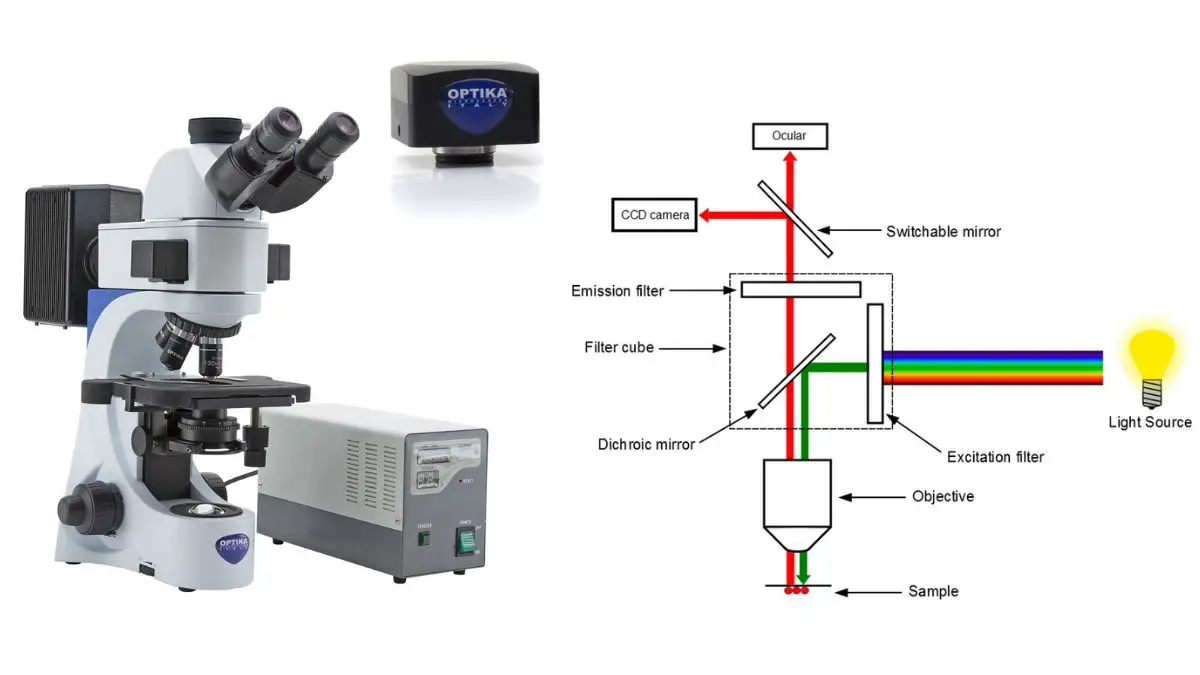
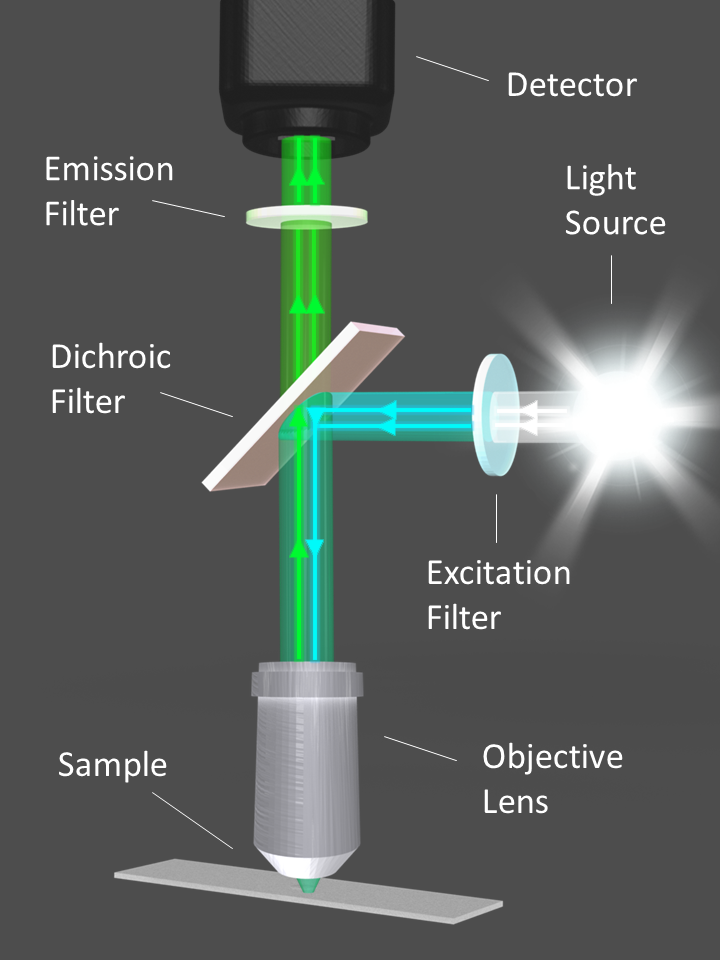
Define fluorescence microscopy. The meaning of FLUORESCENCE is luminescence that is caused by the absorption of radiation at one wavelength followed by nearly immediate reradiation usually at a different wavelength and that ceases almost at once when the incident radiation stops. The cameras used in fluorescence microscopy allow the detection of signal beyond the wavelengths our eyes can see. The difference in colors is called the Stokes shift.
The cameras used in fluorescence microscopy allow the detection of signal beyond the wavelengths our eyes can see. Fluorescent dyes are the chemical substances used in this advanced microscopic method. A substance is said to be fluorescent when it absorbs the energy of invisible shorter wavelength radiation such as UV light and emits longer wavelength radiation of visible light such as green or red light.
Fluorescence microscopy - light microscopy in which the specimen is irradiated at wavelengths that excite fluorochromes microscopy - research with the use of microscopes indirect immunofluorescence - a method of using fluorescence microscopy to detect the presence of an antigen indirectly. Epifluorescence microscopy is widely used in cell biology as the illumination beam penetrates the full depth of the sample allowing easy imaging of intense signals and co-localization studies with multi-colored labeling on the same sample. Fluorescence microscopy is a major tool with which to monitor cell physiology.
Learn about the physical properties. A fluorescence microscope is an optical microscope that uses fluorescence and phosphorescence. It has a number of advantages over other forms of microscopy offering high sensitivity and specificity.
Fluorescence microscopy is a technique whereby fluorescent substances are examined in a microscope. Fluorescence Microscopy Multiphoton n. Meaning pronunciation translations and examples.
Fluorescence microscopy utilizing multiple low-energy photons to produce the excitation event of the fluorophoreMultiphoton microscopes have a simplified optical path in the emission side due to the lack of an emission pinhole which is necessary with normal confocal microscopes. Fluorescence microscope one used for the examination of specimens stained with fluorochromes or fluorochrome complexes eg a fluorescein-labeled. Definition of Fluorescence Microscopy.